Boric Acid– Compounded Vaginal Preparations
Boric acid is a familiar substance to many of us. It is found in many common household goods, but did you know that boric acid can be used as a safe and effective treatment?
Basic Facts
Boric acid is a white powdery substance that belongs to a class of chemicals called Borates. Borates have been used for centuries in multiple uses such as food preservation, cleaning and medicine. Boric acid can be found in naturalmineral deposits all of the world, from the state of Nevada to Tuscany, Italy.
How does it work?
In medicine, it works as an antiseptic by disrupting the cell membranes of microorganisms, such as bacteria and yeast.
Boric Acid Use in Pharmaceuticals
Boric Acid can be found in many pharmaceutical preparations, such as:
Ophthalmic (eye) solutions
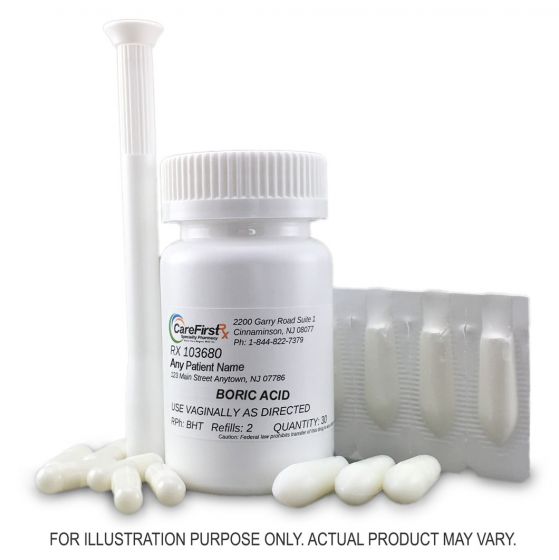
Vaginal capsules and suppositories
Otic (ear) solutions
Topicals for the skin
Vaginitis
The most common boric acid preparations available are vaginal capsules and suppositories.Boric acid is often used for stubborn chronic candida vaginitis. Some women also turn to boric acid if they are allergic to other common treatments, such as nitroimidazole drugs.
Boric acid vaginal capsules and suppositories are easy to use and less messy than other types available on the market.
Common side effects may include:
- Watery discharge
- Mild burning sensation
- Irritation of surrounding skin
- Skin irritation after sexual contact
Other Important Information
Risk of toxicity is very minimal with vaginal preparations when used properly. Overdose can cause toxicity and can cause multiple organ damage. Chronic use may predispose certain individuals.
Discuss sexual activity with your physician before using boric acid. Boric acid vaginal treatment could cause skin irritation or other health problems for your sex partner.
Boric acid should not be used in pregnant or breastfeeding women, unless specifically instructed by a physician.
Boric acid should not be used in children, unless specifically instructed by a pediatrician.
DO NOT use orally, rectally or on open wounds, as this can cause boric acid poisoning.
While boric acid does not commonly interact with other drugs, please inform your physician and pharmacist of any medications (including herbs and supplements), before using boric acid.
Use the medication as prescribed by your doctor. The information provided is not intended to cover all possible uses. This information is generalized and not intended as specific medical advice. If you have questions about the use of your prescription, please contact your prescriber.
References
- https://www.drugs.com/mtm/boric-acid-ophthalmic.html
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/boric_acid#section=Pharmacology-and-Biochemistry
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26026892
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22877600
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1784796/pdf/9812253.pdf