Oral Ketotifen: Some Novel Uses
Ketotifen is a drug used worldwide for the treatment of allergic conditions, most commonly asthma. While the oral tablet form is commercially available in other countries, it is only available in the United States through compounding pharmacies.
How does it work?
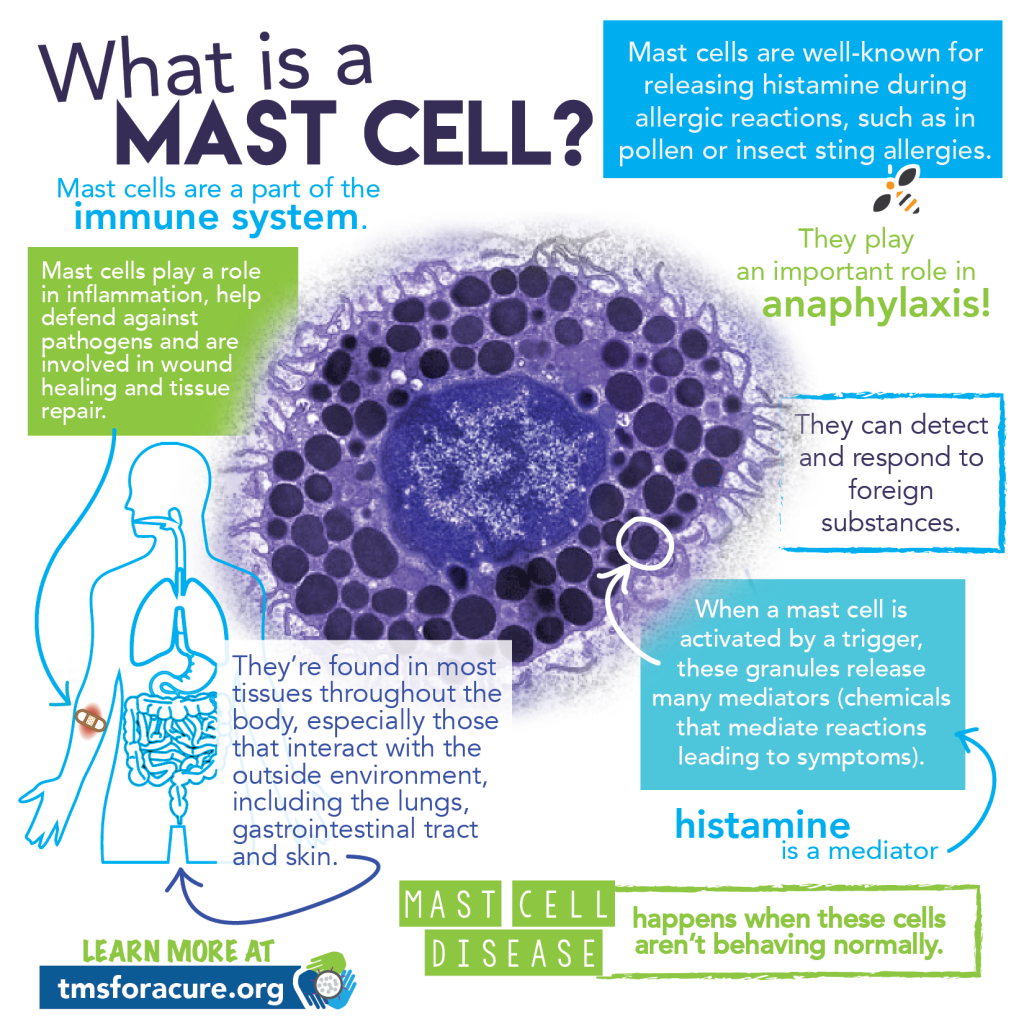
Ketotifen works by preventing inflammation and allergic reactions in your body. When you are exposed to an allergen, specialized cells called mast cells react by releasing chemicals like histamine, cytokines, and other mediators that cause inflammation and your body’s allergic reaction. Ketotifen acts by two major mechanisms: (1) blocking the action of histamine and your body’s reaction to it, and (2) stabilizing mast cells and preventing them from releasing its chemical mediators.
What is it used for?
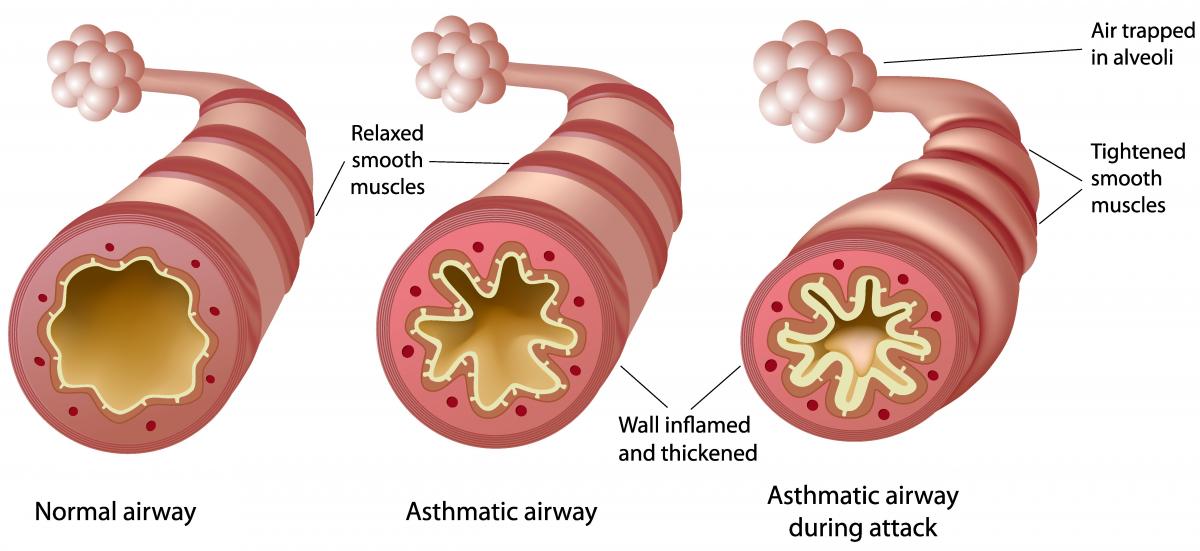
Oral ketotifen is primarily used for people with asthma. Asthma is caused by inflammation of the airways, causing them to narrow and making breathing difficult. Ketotifen can prevent this inflammation and therefore can prevent asthma attacks. It is given in the chronic treatment of asthma (however, it cannot be used to treat an active asthma attack). There is some evidence for the use of oral ketotifen in other allergic conditions too, such as idiopathic anaphylaxis (an allergic reaction without a known cause), mastocytosis (a condition caused by excessive mast cells in the body), and urticaria (hives).
How can I get it?
The oral form of ketotifen is commercially available in Canada, Australia, and many countries in Europe. In the United States, ketotifen is only available over-the-counter as eye drops for itchy eyes caused by allergies. However, oral capsules of ketotifen need to be compounded and are available at specialty compounding pharmacies with a prescription. The dose usually used for asthma is 1 mg twice a day.
References
- Amin K. The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Respir Med. 2012;106:9-14.
- Zaditor™ (ketotifen fumarate) [package insert]. Duluth, GA: CIBA Vision, A Novartis Company; 2009.
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Asthma. Retrieved January 8, 2019, from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/asthma
- Patterson R, Fitzsimons EJ, Choy AC, Harris KE. Malignant and corticosteroid-dependent idiopathic anaphylaxis: successful responses to ketotifen. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997;79(2):138.
- Kettelhut BV, Berkebile C, Bradley D, Metcalfe DD. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of ketotifen versus hydroxyzine in the treatment of pediatric mastocytosis. J allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 May;83(5):866-70.
- Sokol KC, Amar NK, Starkey J, Grant JA. Ketotifen in the management of chronic urticarial; resurrection of an old drug. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013 Dec;111(6):433-436.
- Ketotifen 1 mg. 30 tablets. [image] Available at: www.medicine-online.org/index.php?id_product=2805&controller=product&id_lang=1. [accessed 8 Jan. 2019].
- What is a mast cell infographic. [image] Available at: https://www.naughtylittlemastcells.com/what-is-mast-cell-activation-syndrome/ [accessed 8 Jan. 2019].
- Comparison of normal airway vs asthmatic airway vs asthmatic airway during attack (2015). [image] Available at: http://simplebiologyy.blogspot.com/2015/10/what-is-asthma-what-are-asthma-smptoms-causes-treatments-and-prevention.html [accessed 8 Jan. 2019].



Comments